Peer-Reviewed Publications
Automatic Modulation Classification using Induced Class Hierarchies and Deep Learning
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, Birsen Sirkeci-Mergen
This work focuses on the emerging field of deep learning (DL) methods of automatic modulation classification (AMC) for cognitive radios. In this work, we use induced class hierarchies to decompose the AMC task into sub-tasks, while still maintaining deep architectures for improved classification accuracy.
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, Birsen Sirkeci-Mergen
This work focuses on the emerging field of deep learning (DL) methods of automatic modulation classification (AMC) for cognitive radios. In this work, we use induced class hierarchies to decompose the AMC task into sub-tasks, while still maintaining deep architectures for improved classification accuracy.
Density-Based Clustering of Static and Dynamic Functional MRI Connectivity Features Obtained from Subjects with Cognitive Impairment
D. Rangaprakash, Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, D. Narayana Dutt, Gopikrishna Deshpande
In this work, we show the effectiveness of density-based clustering methods to robustly classify cognitive state based on fMRI images. We compare DBSCAN and OPTICS, and propose a new clustering method, R-CLAN, which successively adds Gaussian noise to the connectivity features to improve classification robustness to noise and outliers.
D. Rangaprakash, Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, D. Narayana Dutt, Gopikrishna Deshpande
In this work, we show the effectiveness of density-based clustering methods to robustly classify cognitive state based on fMRI images. We compare DBSCAN and OPTICS, and propose a new clustering method, R-CLAN, which successively adds Gaussian noise to the connectivity features to improve classification robustness to noise and outliers.
Other Projects
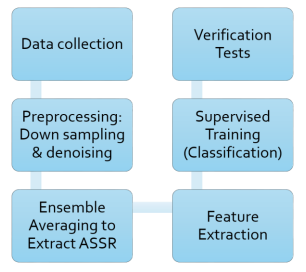
Investigating the 40-Hz Auditory Steady State Response as a Modality for Biometric Verification
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa
How can we verify a user is who they say they are in order to access a secure system? In this work, I explore a novel medical biometric modality – the auditory steady state response (ASSR) – to determine its inter-subject discriminatory power as a biometric verification tool. ASSR, normally used in audiometry to evaluate hearing, is the brain wave response to an amplitude modulated stimulus presented to the ear. Through signal processing and machine learning classification, I show that the ASSR signal is a promising biometric for future security systems.
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa
How can we verify a user is who they say they are in order to access a secure system? In this work, I explore a novel medical biometric modality – the auditory steady state response (ASSR) – to determine its inter-subject discriminatory power as a biometric verification tool. ASSR, normally used in audiometry to evaluate hearing, is the brain wave response to an amplitude modulated stimulus presented to the ear. Through signal processing and machine learning classification, I show that the ASSR signal is a promising biometric for future security systems.
A Work-Stealing Quicksort Algorithm for GPUs
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, Sarmad Saeed
Data parallel tasks are well-mapped to graphic processing units (GPUs). What about workloads that are parallel on the task level? While task-parallelism has traditionally been accomplished on multi-core CPUs, we explore a work-stealing approach in CUDA to load balance quicksort--a highly task-parallel algorithm-- on the GPU.
Toluwanimi Odemuyiwa, Sarmad Saeed
Data parallel tasks are well-mapped to graphic processing units (GPUs). What about workloads that are parallel on the task level? While task-parallelism has traditionally been accomplished on multi-core CPUs, we explore a work-stealing approach in CUDA to load balance quicksort--a highly task-parallel algorithm-- on the GPU.